The “fountain of youth” is a region near the Milky Way’s central black hole that’s full of newborn stars. The James Webb Space Telescope and other galactic surveys have confirmed the existence of this stellar “fountain of youth”.
The “fountain of youth” is made up of:
- Newborn stars that shouldn’t exist
- Water ice
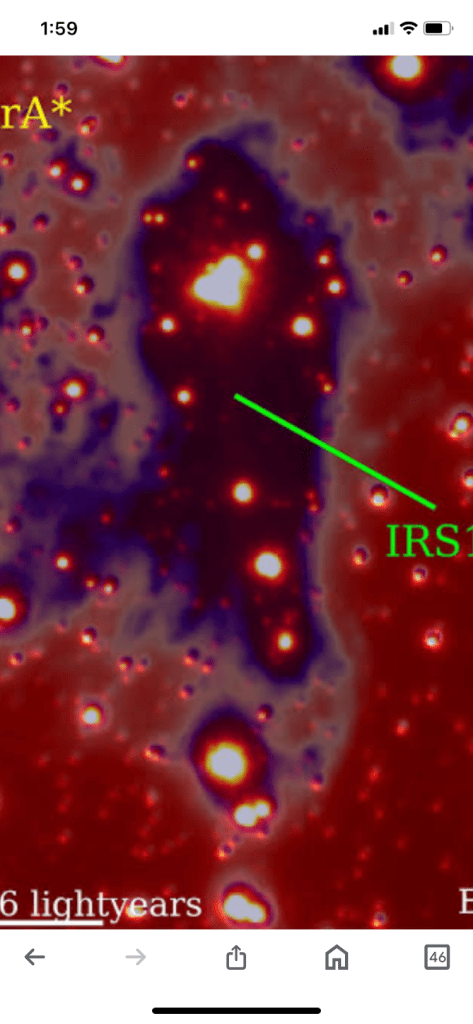
The “fountain of youth” is located in IRS13, which is home to many young stars.
The Milky Way’s central supermassive black hole is Sagittarius A*. It has a mass of 4.154±0.014 million solar masses.
Scientists can’t directly observe black holes with telescopes that detect x-rays, light, or other forms of electromagnetic radiation. However, they can infer the presence of black holes and study them by detecting their effect on other matter nearby.
The James Webb Space Telescope and other galactic surveys have confirmed there’s a stellar “fountain of youth” birthing new stars near the Milky Way’s central black hole.
Near the galaxy’s supermassive black hole, strong radiation and gravitational forces create inhospitable conditions for new star formation.
A particular cluster of young stars, known as IRS13, was discovered over 20 years ago.
The discovery was made by an international team of researchers, led by University of Cologne Institute of Astrophysics researcher Florian Peißker, that examined a star cluster close to our galaxy’s central supermassive black hole, Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*).
The discovery of such an abundance of youthful stellar bodies at the heart of the Milky Way is shocking because it was previously thought that high-energy radiation and immense tidal forces generated by gravity in this central region (and near Sgr A*, which has a mass equivalent to 4.3 million suns) would disrupt star formation. That should have prevent young stars from gathering around Sgr A* and in the vicinity of the galactic center
Is there a black hole in the centre of Milky Way
Yes, there’s a supermassive black hole in the center of the Milky Way. It’s located in an area called Sagittarius A. Astronomers can locate it by studying radio emissions from the region and observing how stars revolve around it.
Sagittarius A* is less luminous than other black holes at the centers of galaxies. This means that the Milky Way’s central black hole hasn’t been actively consuming material around it.
In 2022, astronomers captured the first image of Sagittarius A*. This image provides evidence that the object is indeed a black hole. It also provides clues about how these giants work.
Best clothes on discount on Amazon
https://94b1aqmi1xpu73k5lmyet09se7.hop.clickbank.net
https://325ffnofax–fridsapnwvl6ji.hop.clickbank.net