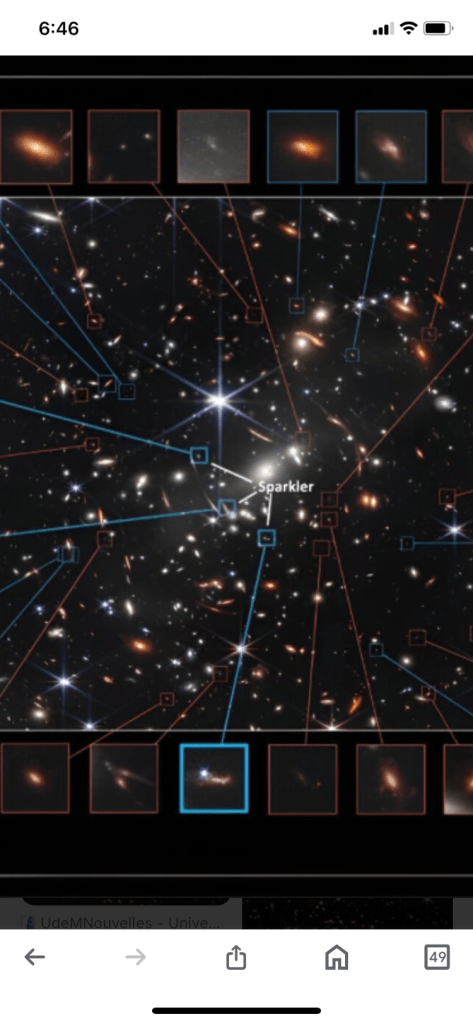
Astronomers have measured the distances of nearly 200 galaxies from Earth using the JWST’s NIRISS instrument. The galaxies are located eight to 10 billion light years away.
How astronomers measured the distances
- Redshifts The team measured the “redshifts” of the galaxies. Redshifts are shifts in the spectra of very distant galaxies toward longer wavelengths. They are a precise measurement of a galaxy’s distance based on the unique chemical signatures seen in its spectra.
- NIRISS instrument The NIRISS instrument can measure the redshifts of hundreds of galaxies at once.
What the study found
- The study uncovered many new galaxies in the SMACS 0723 cluster. The light from these galaxies has taken more than 4 billion years to reach us.
- The study will be a valuable resource for the astronomical community and open up new avenues of research.
- CANUCS astronomers will be able to improve upon their galaxy redshift catalog during Webb’s second year of scientific operations.
On July 11, 2022, the very first image taken by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) was released to the general public. It’s called Webb’s First Deep Field, centered on a cluster of galaxies named SMACS 0723
Astronomers use different methods to measure the distance of galaxies depending on their distance:
- Surface brightness fluctuations (SBF) Astronomers can use SBF and the color of a galaxy to calculate its distance from Earth. Supernovae For more distant galaxies, astronomers use the rate at which supernovae brighten and fade to calculate their distance. Parallax For stars in other galaxies and far away stars, astronomers use the method of parallax to find distance. Cepheid variable stars For stars in our galaxy, astronomers use Cepheid variable stars as standard candles. Type 1a supernova For very far away galaxies, astronomers use Type 1a supernova as standard candles. Redshift Astronomers measure the speed of a galaxy by analyzing its redshift. Brightness of red giant stars Astronomers can measure the brightness of red giant stars when they reach the brightest phase during their stellar evolution. This technique gives very precise distances when galaxies are relatively close. Sending a signal from Earth Astronomers can send a signal from Earth and measure the reflection off of the object’s surface. Sending a spacecraft to the object Astronomers can send a spacecraft to the object that either reflects or actively transmits back towards Earth.
Edwin Hubble discovered that galaxies are actually “island universes” and that the universe is expanding.
Hubble’s discoveries
- Hubble’s law: Hubble’s law states that the farther away a galaxy is from Earth, the faster it moves away from us. This means that the universe is expanding.
- The spiral nebula Andromeda is a galaxy: Hubble announced in 1924 that the spiral nebula Andromeda is a galaxy.
- The Milky Way is one of many galaxies: Hubble announced in 1924 that the Milky Way is one of many galaxies in the universe.
Hubble’s life
- Hubble was born on November 20, 1889.
- He began classifying all known nebulae and measuring their velocities from the spectra of their emitted light.
- He announced his findings in 1929.
- The Hubble Space Telescope is named after him.
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has captured images of over 45,000 galaxies in one frame. The JWST captured the image as part of the JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey program. The image was of a portion of the sky known as GOODS-Sout.
The JWST has also:
- Revealed 25,000 galaxies in its COSMOS-Web survey
- Discovered 717 ancient galaxies
- Detected what appear to be six massive ancient galaxies, which astronomers are calling “universe breakers”
- Discovered hundreds of galaxies that existed when the Universe was less than 600 million years old
- Seen about 25,000 galaxies in a single image, dramatically surpassing the nearly 10,000 shown in the Hubble Space Telescope’s Ultra Deep Field Survey
