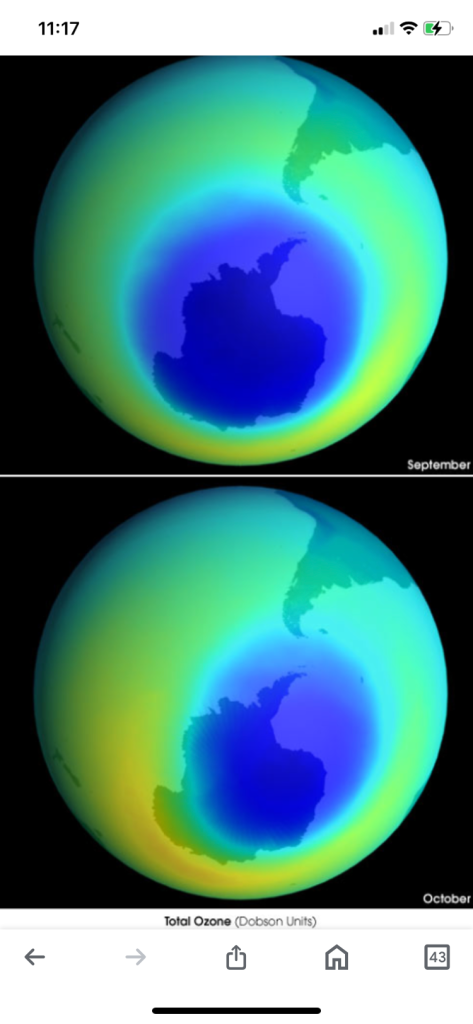
A new study published in Nature Communications says that the ozone hole over Antarctica has grown larger and thinner throughout most of the spring. The hole has been massive in the last four years, despite making a recovery in area and depth since the 2000s
The study suggests that the mesosphere, the layer of the atmosphere above the stratosphere, might be responsible for the decline in ozone. The ozone around the hole’s core has decreased by over 26% since 2004. The researchers argue that this decline can be attributed to changes in the mesosphere that impact the polar vortex. The polar vortex is the mass of cold air that circles the South Pole.
Other factors that might be responsible for the depletion include:
- Tiny, airborne particles emitted from wildfires and volcanoes
- Changes in solar cycle
A United Nations report has found that the ozone layer is healing at a pace that will fully mend the hole over Antarctica in about 43 years
The ozone hole over the Antarctic has not only grown larger but also thinner throughout most of the spring, according to a new study. Despite making a recovery in area and depth since the 2000s, the Antarctic ozone hole has been massive in the last four years, the study published in Nature Communications noted.( source google)
Chlorine gas plays the most important role in ozone depletion. Chlorine can combine with bromine to cause ozone depletion. Some chemical compounds can release chlorine and bromine into the atmosphere.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are also a major cause of ozone depletion. CFCs are released from refrigerators, air coolers, foam-blowing things, solvents, spray aerosols, and air-conditioners. When these CFCs reach the stratosphere, they break down ozone (O3) into plain oxygen (O2).
Other pollutants that deplete the ozone layer include: HFCs, Methyl bromide.
The ozone layer protects life on Earth by absorbing 97–99% of the sun’s ultraviolet radiation. This radiation can damage DNA and cause sunburn, skin cancer, and glaucoma
Ozone depletion increases the amount of UV radiation that reaches Earth’s surface. This can cause:
- Skin cancer
- Cataracts
- Impaired immune systems
- Genetic damage
- DNA damage and mutation
- Skin burn
- Quick aging
- Weak immune system
- Global warming
Ozone depletion also damages phytoplankton and hinders photosynthesis in plants. This can reduce agricultural productivity
Ozone depletion has devastating effects on human health, animals, plants, microorganisms, and air quality.
Human health
Skin cancer, Cataracts, Weakened immune systems, Quick aging, Sunburns, Skin diseases.
Plants and animals
- Reduced crop yield
- Disruptions in the marine food chain
- Loss of biodiversity
- Extinction of many species of birds
Environmental effects
- Global warming
- Damage to vegetation and ecosystems
- Interference with the photosynthesis process
The main cause of ozone depletion is chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). CFCs are chemical compounds used in many products, including: Air conditioners, Refrigerators, Spray cans, Solvents, Spray aerosols.
CFCs are broken down by ultraviolet radiation in the stratosphere, releasing chlorine atoms. These chlorine atoms combine with ozone to form chlorine monoxide and free oxygen.
The strongest depletion of ozone occurs above Antarctica. This is because chlorine and bromine derived from human-produced compounds attach to high-altitude polar clouds each southern winter. As the sun rises at the end of winter, these reactive chlorine and bromine initiate ozone-destroying reactions.
Ozone depletion can lead to increased amounts of UV radiation reaching the Earth. This can cause more cases of skin cancer, cataracts, and impaired immune systems.
Here are some ways to protect the ozone layer:
- Reduce vehicle use Use bicycles, walk, or take public transportation instead.
- Use eco-friendly products Use cleaning products that are eco-friendly. Buy air conditioning and refrigeration equipment that don’t use HCFCs as refrigerants. Buy aerosol products that don’t use HCFCs or CFCs as propellants.
- Avoid ozone-depleting substances Avoid using pesticides, nitrous oxide, and ODS. Avoid gases that are dangerous to the ozone layer, like CFCs, halogenated hydrocarbon, methyl bromide, and nitrous oxide.
- Dispose of old appliances properly Dispose of old fire extinguishers and cooling appliances that contain ozone-depleting substances.
- Maintain appliances Regularly inspect and maintain air conditioning and refrigeration appliances to prevent refrigerant leakage.
Other ways to protect the ozone layer include:
- Eating less meat
- Buying local
- Using renewable sources of energy
- Recycling and reusing
The ozone layer absorbs some of the sun’s radiation, including UVB, which can be harmful. The hole in the ozone layer over Antarctica is expected to close by the 2060s.
https://bfaddqjkd5ntjx8e4hea-9n804.hop.clickbank.net