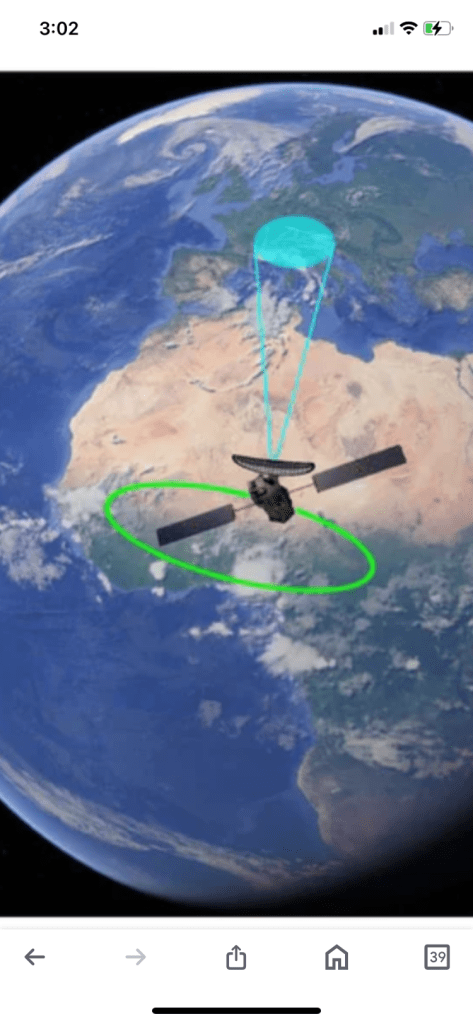
According to a paper, there is one orbitthat is particularly favorable for space-based interferometers. Interferometry uses the wave property of light.
Here are some orbit configurations for space interferometers:
- Two satellites: Two circular orbits of R1 = 7500 and R2 = 8000 km, one of which is retrograde
- Three satellites: One regular orbit of 22500 km
- Four satellites: One retrograde orbit of 23000 km
The paper proposes a combination of regular and retrograde near-Earth circular orbits to achieve faster coverage.
The Space Interferometry Mission (SIM) was canceled in 2010. One of its main goals was to find Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of nearby stars.
The Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) is expected to launch in 2037. It will have three 2.5-million-kilometer arms.
In a paper published on 18 November in Astronomy & Astrophysics Journal, author Takahiro Ito from the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science in Japan takes a look at the possible orbits that the interferometers might be put in and concludes that maintaining precise positioning in geocentric (Earth centred) orbit
An astronomical interferometer is made up of two or more telescopes that combine their signals. The resolution of an interferometer is equal to the resolution of a telescope with a diameter equal to the maximum separation between the individual telescopes.
Interferometers can make observations that are not possible with a single telescope. They combine the light collected by multiple telescopes, which makes the light brighter. This allows telescopes to act as one larger “virtual telescope”. Interferometry can make it possible to see fainter objects in more detail.
The Large Binocular Telescope Interferometer (LBTI) is a ground-based instrument that connects two 8-meter class telescopes on Mount Graham in Arizona. The LBTI is the largest single-mount telescope in the world.
Interferometry can provide higher angular resolution than conventional telescopes. This is because it combines light from multiple telescopes to create a larger aperture. The result is a pattern of alternating light and dark bands called interference fringes.
Interferometry is also used in radio astronomy. Radio astronomers can combine signals from separate radio telescopes to create high-resolution images.
Interferometers have other applications, including:
- Surface measurement: Interferometry is highly sensitive to surface topography.
- Distance measurement: Interferometers can measure distance and thickness in the sub-nanometer range.
- Refractive index changes: Interferometers can measure refractive index changes.
- Surface properties: Interferometers can measure surface properties
Laser interferometers are often the most accurate interferometers available. They are commonly used to measure:
- Distances
- Refractive index changes
- Surface properties
Here are some accuracies for different interferometers:
- Zygo interferometer: ±0.0002 accuracy for measuring the refractive index of liquids
- Two-color interferometer: 0.15 ppm accuracy for measuring changes in air refractive index
- Interferometer for measuring displacement and distance: 0.02 microm accuracy for displacement and 100 microm accuracy for distance over a few meters
Interferometry is the most precise method for measuring displacement accurately to within a few meters(all article source google)
https://5c68bmmh3yut8tdb0ci9ucnaao.hop.clickbank.net
Nice post
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thanks sir🙏
LikeLike