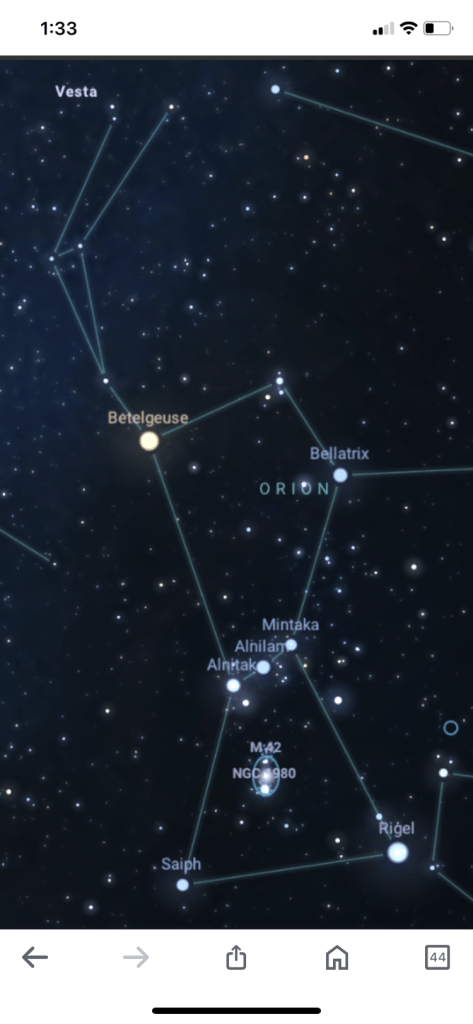
On December 6, 2023, the asteroid Vesta appeared in northern Orion, near the feet of Gemini, the Twins. Vesta is the third-largest and brightest asteroid, and is a V-type asteroid or Vestoid. Vesta is the largest Vestoid, which is a type of asteroid with the same spectral type as 4 Vesta
Vesta will be visible in Orion through binoculars throughout December 2023. Most asteroids are not visible without a powerful telescope or with the naked eye.
Starlike Vesta — the brightest and third-largest asteroid — appears in northern Orion near the feet of Gemini, the Twins, on December 6, 2023. During the next few weeks, it moves about a quarter-degree to the west-northwest each night and passes by several bright stars that aid in finding it.
The asteroid Vesta appeared in northern Orion on December 6, 2023, near the feet of Gemini. Vesta is the third-largest and brightest asteroid
Vesta is highest overhead around 1–2 AM, which is ideal for telescope viewing. However, it can be observed as early as 10 PM, when it will appear about halfway up the eastern sky. Vesta can be located between the raised arm of Orion and the leg of Castor in Gemini.
Vesta will reach opposition on December 21, 2023, when it can be found shining at mag. +6.6 among the stars of northern Orion.
Vesta was discovered by the German astronomer Heinrich Wilhelm Matthias Olbers on March 29, 1807. It is named after Vesta, the virgin goddess of home and hearth from Roman mythology.
Vesta is located approximately 100 million miles from Earth in the solar system’s main asteroid belt. Scientists believe the asteroid formed prior to the planets, making it one of the oldest objects in space that’s within our reach
Vesta orbits the sun between Mars and Jupiter, within the asteroid belt. It orbits the sun once every 3.63 years, with a mean distance of 2.36 astronomical units (AU
Vesta is the second most massive body in the asteroid belt, accounting for almost 9% of the total mass of all asteroids. It has a diameter of about 330 miles.
Vesta is the second largest asteroid in the solar system’s asteroid belt, with only Ceres being larger
Vesta is the brightest asteroid in the sky and is occasionally visible to the naked eye from Earth. It’s the only main-belt asteroid that can be seen without any aid. When it’s at its brightest, Vesta is just barely visible to the naked eye from a dark location. However, it can be easily seen with a small pair of binoculars
Vesta has one of the largest brightness ranges of any rocky body in our solar system. The bright material appears to be native rocks, while the dark material is believed to have been deposited by other asteroids crashing into Vesta
Vesta is not a planet because it’s not quite large enough to be considered a dwarf planet. It’s also irregular in shape and orbits the sun on its own
Vesta is a protoplanet, which is a dense, layered body that orbits the sun and formed in the same way as Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. Unlike most asteroids, Vesta has separated into crust, mantle, and core, much like Earth.
Scientists believe that Vesta never made it to full planethood because of Jupiter. When the giant gas planet formed, it perturbed the orbits of nearby bodies like Vesta
The giant asteroid is almost spherical, and so is nearly classified a dwarf planet. Unlike most known asteroids, Vesta has separated into crust, mantle and core (a characteristic known as being differentiated), much like Earth
Orion is a prominent set of stars visible during winter in the northern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the 88 modern constellations; it was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy. It is named for a hunter in Greek mythology
Orion’s Belt or the Belt of Orion, also known as the Three Kings or Three Sisters, is an asterism in the constellation Orion. It consists of three bright stars. They are Alnitak, Alnilamand Mintaka
Orion is named after a hunter in Greek mythology. In one myth, Artemis falls in love with Orion and is tricked by her brother Apollo into killing him with an arrow. Artemis begs Ascelpius to save Orion, but Zeus kills Ascelpius as he is trying. Gaia (Apollo in some versions) objects and sends a giant scorpion to kill Orion. After his death, the goddesses ask Zeus to place Orion among the constellations.
Orion has more than 60 stars, including the bright stars Rigel and Betelgeuse, the Orion Nebula, and Orion’s Belt. Rigel is a blue giant and the brightest star in Orion, while Betelgeuse is a red super giant star and the second brightest star.
To find Orion, look for three bright stars close together in an almost-straight line. These stars form Orion’s belt. Two brighter stars to the north mark his shoulders, and two more to the south represent his feet
Orion is best seen between latitudes 85 and minus 75 degrees. It’s most visible in the evening sky from January to March, winter in the Northern Hemisphere, and summer in the Southern Hemisphere.
You can also use Orion’s Belt to find other stars:
- Canis Major Use the belt stars to point down to Canis Major, which is the brightest star in the night sky, Sirius.
- Taurus Use the belt stars to point up towards Taurus, which is represented as a bull.
- Betelgeuse Once you’ve found Orion’s Belt, look a short way above the top left of the Belt stars to find Betelgeuse, a particularly bright and reddish star.
The Orion Nebula is located in the constellation of Orion the Hunter. It’s visible with the naked eye just below the three bright stars that form the belt of Orion. The middle star of the Sword of Orion looks a little fuzzy, and is actually the Orion Nebula.
According to Space.com, Vesta will be visible all night long on December 21, 2023, and will shine at its brightest for the year. Vesta will be opposite the sun in the sky, making it visible to binoculars and small telescopes
(Full article source google)
https://7ff90dejbv1461ih4mkz-8gffo.hop.clickbank.net