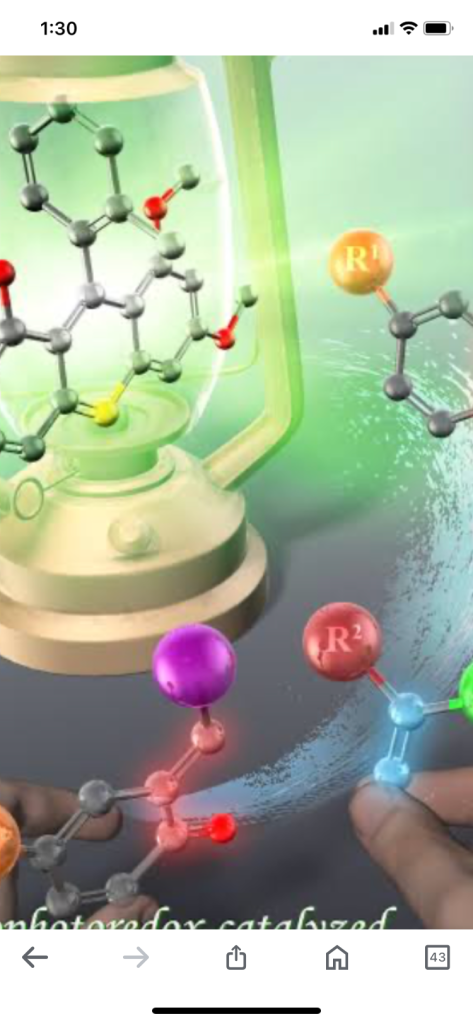
MIT chemists have synthesized colorful organic molecules called acenes. Acenes have potential applications in light-emitting diodes and semiconductors.
The chemists improved the stability of acenes, which allowed them to synthesize acenes of varying lengths. The new approach allowed them to create molecules that emit red, orange, yellow, green, or blue light.
Acenes could also be used in solar cells and organic light-emitting diodes.
Organic synthesis is the process of constructing organic molecules, which are primarily made of carbon. This process involves:
- Mixing reactants in a reactor
- Supplying heat energy if the reaction is slow, or cooling the reactor if the reaction is highly exothermic
- Separating products
The synthesis of organic compounds can be a multi-step process. It involves:
- Constructing the carbon framework of the desired molecule
- Introducing, removing, or transforming functional groups
A total synthesis is the complete chemical synthesis of complex organic molecules from simple precursors. This can be accomplished using either a linear or convergent approach.
Organic synthesis is a fundamental concept in organic chemistry and plays a crucial role in many industries. It involves the design and conceptualization of synthetic routes to simplify and facilitate the production of organic molecules.
Here are some examples of organic synthesis:
- Aspirin: This organic compound comes from the bark of the willow tree.
- Synthetic organic polymers: These include low density polyethylene (LDPE), high density polyethylene (HDPE), polypropylene (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polystyrene (PS), nylon, Teflon, and thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU).
- Polymers: These are large molecules made of many small repeating molecules. Thermoplastics are a type of polymer that can be reshaped and molded at a certain temperature.
Organic synthesis is also known as synthetic organic chemistry. It involves replicating molecules that naturally exist in living creatures and creating similar synthetic ones in a laboratory.
Acenes are chains of fused carbon-containing rings with unique optoelectronic properties. They are also known as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Acenes have received considerable research attention for use as semiconductors in organic optoelectronic applications. These applications include:
- Field effect transistors (OFETs)
- Photovoltaics
- Light-emitting diodes (OLEDs)
- Organic photovoltaic (OPV) devices
- Spintronic devices
Acenes are rich in sharable electrons and can efficiently transport an electric charge. They have a small electronic gap and high-electron mobility, making them attractive materials in organic electronics.
Acenes can also be tuned to emit different colors of light, which makes them good candidates for use in organic light-emitting diodes.
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are used to illuminate objects and places. They are compact, consume low energy, have an extended lifetime, and are flexible in terms of use in various applications
Chains of fused carbon-containing rings have unique optoelectronic properties that make them useful as semiconductors. These chains, known as acenes, can also be tuned to emit different colors of light, which makes them good candidates for use in organic light-emitting diodes
(Full article source google)
https://ec384lfg88vzb2k909v-tamg1s.hop.clickbank.net