In 2016, astronomer Jennifer van Saders discovered that some stars don’t slow down with age as astronomers previously thought. The rotations of the stars slowed down as expected until they reached the age of the sun, after which the rotations leveled out.
Rotation is a useful tool for dating young stars, but is less useful for older ones. For stars older than the sun, other methods are better.
Here are some other methods used to determine the age of a star:
- Color-magnitude diagram A graphical model that relies on theoretical models to determine how stars evolve and what physical properties they should have.
- Gyrochronology A method used to determine the age of field stars by measuring their rotation rate and comparing it with the rotation rate of the sun.
As stars spin, they exhale a constant breath of charged particles that latch on to the star’s powerful magnetic field. Like a ballet dancer extending their arms, the magnetized stellar wind gradually slows a star’s rotation
As stars age, they change in brightness and color. Younger stars appear bluer, while older stars appear redder. This is because stars run out of hydrogen to burn as they age, which reduces the energy they emit.
Stars also expand as they age, consuming the energy generated by the fires burning in their cores. Their atoms are transformed from the original hydrogen to atoms of increasingly complex structure and weight.
Stars follow different paths as they age, depending on their mass. Smaller stars, like our Sun, live long lives. As they start to run out of hydrogen fuel in their core, they expand and turn red, becoming red giants.
After stars become red giants, their cores eventually become hot enough to produce energy by fusing helium to form carbon.
A star like our sun is calculated to have a total stable life-span of around 10 billion years. The sun is now a bit less than half that age.
Astronomers have recently discovered that some stars maintain a constant rotational speed for billions of years, even though they previously thought stars would slow down with age.
Young stars rotate quickly and slow down as they age. This is a useful tool for dating young stars, but is less useful for older ones.
Gyrochronology is a method used to determine the age of field stars by measuring their rotation rate. This rate is then compared with the rotation rate of the Sun, which serves as a precalibrated clock for this measurement
Stars may maintain a constant rotational speed for billions of years due to a midlife change in their magnetic field.
A star’s magnetic field drives its stellar wind, which carries mass and angular momentum away from the star. This contributes to the star’s slowdown.
Asteroseismologists have confirmed that older stars rotate faster than expected. This is due to a process called “magnetic braking”, where the spin slows down as stars grow older.
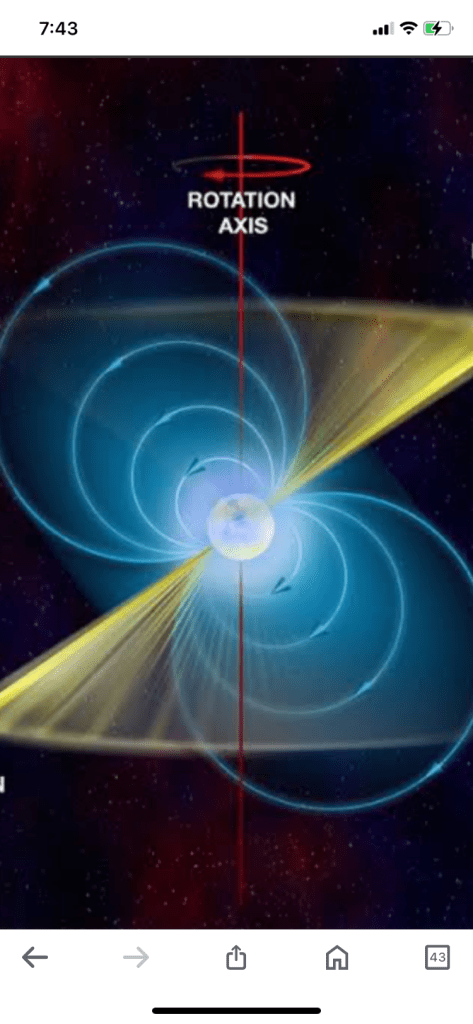
Neutron stars are believed to rotate at a very high speed due to the “conservation of angular momentum during the collapse of the iron core”
According to Scientific American, astronomers have discovered that stars maintain a steady spin for billions of years halfway through their lives. This is due to a change in their magnetic field, which interacts with the stellar wind. As the wind moves away from the star, its angular speed decreases. The star’s magnetic field interacts with the wind, which applies a drag to the stellar rotation.
The evolution of a star’s rotation rate is caused by structural changes in the stellar interior and the gain and loss of angular momentum
Stars maintain a state of stability for long periods of time due to a balance between two forces:
- Inward gravity: The force that pulls the star’s mass inward
- Outward pressure: The force created by heat energy due to fusion reactions
This balance is called hydrostatic equilibrium. As long as the star has enough fuel in its core to continue its fusion reaction, the star will maintain equilibrium and stay a main sequence star.
A main sequence star is stable because of a balance between gravity and nuclear fusion.
Here’s how it works:
- The star contracts until its interior is hot enough for nuclear reactions to start among hydrogen atoms.
- The interior becomes a stable heat source, radiating light and creating enough outward pressure to counterbalance the inward force of gravity.
- The outflow of energy from the central regions of the star provides the pressure necessary to keep the star from collapsing under its own weight.
- The radiation and heat from this reaction keep the force of gravity from collapsing the star.
The Sun is at this stable phase in its life.
According to worldnewsera.com, astronomers have discovered that stars maintain a steady spin for billions of years, around halfway through their lives.
Here’s some more information about stars and their magnetic fields:
- Magnetic fields Stars emit a constant stream of charged particles that attach to their magnetic field. This magnetized stellar wind slows down the star’s rotation.
- Neutron stars Neutron stars slow down over time as their rotating magnetic fields radiate energy. This is called spin down.
- Magnetic fields of dead stars Recent observations have shown that the magnetic fields of neutron stars can persist long after the star has gone supernova.
- Red dwarfs Red dwarfs are the most numerous stars in the universe and have lifespans of tens of billions of years.
- Hypergiants Hypergiants are the most massive stars, and can be 100 or more times more massive than the sun.
Here are some types of stars that can remain as such for billions of years:
- Red dwarfs These stars are the most numerous in the universe and can live for tens of billions of years.
- Main sequence stars These stars remain stable and shine for millions or billions of years after their mass stabilizes.
- White dwarfs These stars are stable because the inward pull of gravity is balanced by the electrons in the core of the star repulsing each other. They can radiate their remaining heat into space for many billions of years.
Neutron stars are another type of star that can live forever. They have exceptionally strong magnetic fields and rotate extremely rapidly. Many neutron stars are observed through periodic radio waves they emit, called pulsars.
Best woman clothes on heavy discount on Amazon