NASA is investing in a new nuclear rocket concept for space exploration and astrophysics. The agency has committed up to $300 million to the DRACO partnership, which includes the design and development of a nuclear-powered engine
NASA has also hired Lockheed Martin to design, build, and test a nuclear-powered rocket for space travel. The technology could reduce the minimum time for a manned trip to Mars from seven months to 45 days.
NASA is also working on a project called DRACO, or Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations. The project aims to test nuclear thermal propulsion (NPT) in space.
NASA is also planning astrobiology missions to Venus and Mars to search for evidence of extraterrestrial life.
NASA Invests in New Nuclear Rocket Concept for the Future of Space Exploration and Astrophysics. In the coming years, NASA plans to send several astrobiology missions to Venus and Mars to search for evidence of extraterrestrial life
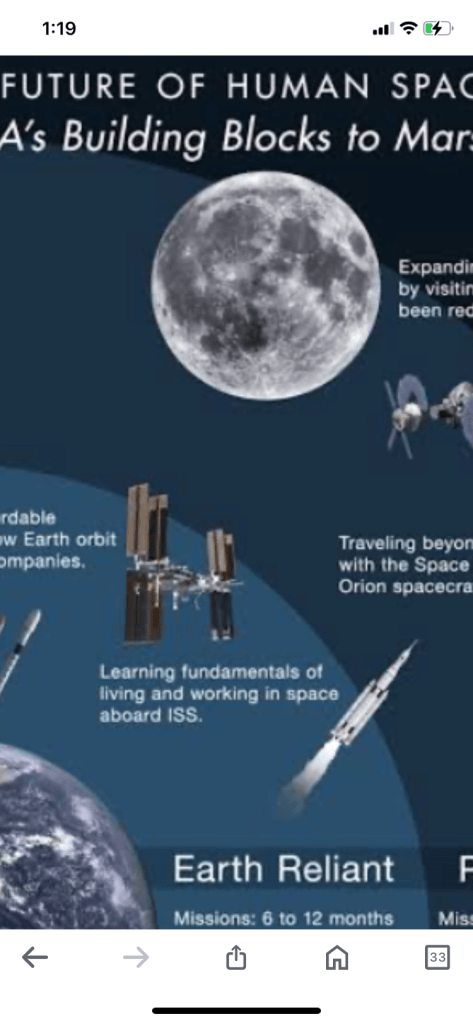
humans on the moon by 2025 to establish a base camp. This long-term presence will help NASA prepare for longer and more distant missions, including a crewed flight to Mars.
NASA also plans to send robotic probes to explore the solar system, including the moons of Jupiter and other outer planets. NASA also plans to launch new space telescopes to search for planets beyond our solar system.
NASA’s Artemis program involves several flights of the Orion spacecraft and lunar landings from 2022 to 2028. The Artemis II mission, scheduled for late 2024, will fly astronauts around the moon, taking them the furthest from Earth since the 1970s.
NASA also plans to send the first humans to Mars by 2030. SpaceX also wants to send crewed missions to Mars to set up a human colony.
NASA says that space exploration provides a new perspective to study Earth and the solar system. It also advances new technologies that improve our daily lives, and inspires a new generation of artists, thinkers, tinkerers, engineers, and scientists.
NASA has several projects planned for 2024, including:
- Artemis II: The first crewed Artemis mission around the moon, scheduled for September 2025.
- Artemis III: The first astronauts will land near the lunar South Pole in September 2026.
- Artemis IV: The first mission to the Gateway lunar space station, scheduled for 2028.
- Europa: A mission to one of Jupiter’s icy moons.
- Earth climate satellites: Launching two new satellites.
- Quiet supersonic aircraft: Demonstrating a quiet supersonic aircraft. NASA’s Artemis program also includes:
- Landing the first woman and first person of color on the moon.
- Establishing a permanent base on the moon to facilitate human missions to Mars.
- Using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before. NASA is also developing new deployable structures and materials technologies for solar sail propulsion systems.
In 2024, NASA plans to:
- Launch the Europa Clipper: In October, NASA plans to launch the Europa Clipper to study Jupiter’s moon Europa.
- Launch the Hera mission: NASA plans to launch the Hera mission to the Didymos asteroid to study the effects of the Double Asteroid Redirection Test.
- Launch the EscaPADE mission: NASA also plans to launch the EscaPADE mission to Mars in 2024.
- Test Artemis moon rockets: NASA has begun testing future Artemis moon rockets in 2024.
- Send spacecraft to the moon: NASA plans to send up to four spacecraft to land on the moon in 2024 as part of its Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program.
- Conduct simulated Mars missions: NASA plans to conduct four simulated missions to Mars in 2024 using HERA. Each mission will include a different crew of four astronaut-like research volunteers. NASA also plans to:
- Launch the VIPER mission to search for water on the Moon.
- Launch the Lunar Trailblazer and PRIME-1 missions.
- Launch JAXA’s Martian Moon eXploration mission.
- Launch ESA’s Hera mission.
Nuclear propulsion uses radioisotope decay or nuclear fission reactors to power spacecraft propulsion and other space missions. Nuclear propulsion systems have a higher energy density than conventional chemical propulsion systems, allowing for faster and more efficient travel
Nuclear thermal propulsion is a concept that uses nuclear fission reactors to provide thrust for spacecraft. The system works by transferring heat from the reactor to a liquid propellant, which converts the liquid into a gas. The gas then expands through a nozzle to provide thrust and propel the spacecraft.
NASA has been studying the concept of nuclear thermal propulsion for decades. The concept would use the nuclear decay of a radioactive material in a radioisotope electric propulsion system to propel a spacecraft to extremely high speeds. This would allow for the study of distant and fast-moving objects in the solar system in relatively short timeframes.
The hypothesis of stimulated acceleration of nuclear decay (SAND) may shorten the travel time to Mars to within 20 days.
NASA plans to send multiple astrobiology missions to Venus and Mars in the coming years to search for evidence of extraterrestrial life. These missions will take place alongside crewed missions to the Moon and the first crewed missions to Mars.
NASA has selected two missions to study Venus, each with a budget of about $500 million. The missions are expected to launch between 2028 and 2030. The DAVINCI+ mission will measure the composition of Venus’ atmosphere to determine how it formed and evolved, and whether the planet ever had an ocean.
In addition, the first private mission to Venus is scheduled for launch in January 2025. The mission will explore the chemistry that might be a sign of life.
Astrobiology is the study of life in the universe. It aims to understand the origin of life on Earth and search for signs of life elsewhere in the universe
Please like subscribe comment your precious thoughts on universe discoveries (a perfect destination for universe new discoveries and science discoveries)
Full article source google
https://7731arfkz8o2h3ae3fbonbrq08.hop.clickbank.net