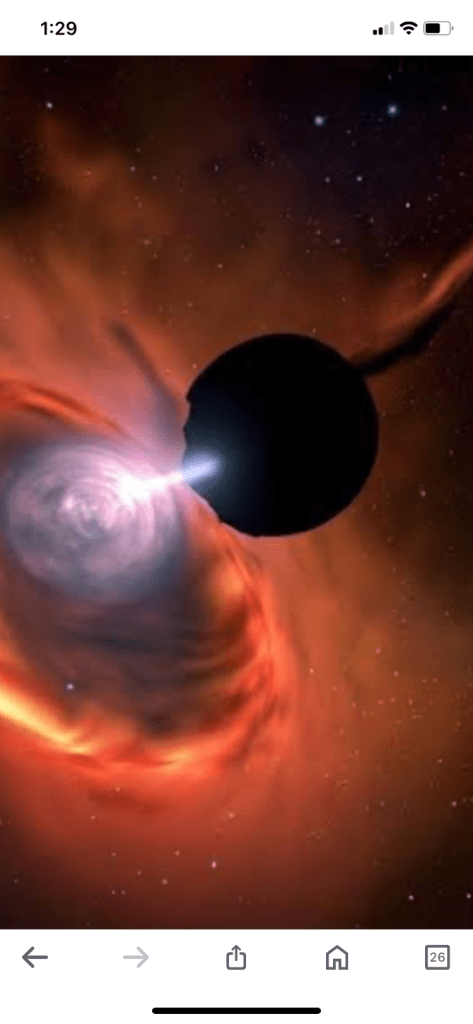
a black hole in one galaxy has cleared out its neighborhood by spitting out material at high speeds.
Black holes grow by pulling in nearby matter with their gravity. This material collects in an accretion disk and waits to cross the event horizon. Once something crosses the event horizon, it’s gone forever.
Black holes are black because nothing, not even light, can escape them. When they’re not actively feeding, they lose mass and energy as radiation.
The distant SMBH sent so much material from the disk out into space at high speed that it cleared out all of the gas in the region. That stifled star formation in the galactic centre. The discovery is presented in new research in The Astrophysical Journal Letters
Beyond a certain region, not even light can escape the powerful tug of a black hole’s gravity. And anything that ventures too close—be it star, planet, or spacecraft—will be stretched and compressed like putty in a theoretical process aptly known as spaghettification
Black holes can affect their surroundings in a few ways:
- Gravity: Black holes’ intense gravity pulls on nearby objects. Astronomers can detect black holes by looking for objects that move erratically around them.
- Orbits: Objects can orbit black holes. Astronomers can detect black holes by looking for stars that appear to orbit nothing.
- Matter: Matter near a black hole can be stretched, pulled apart, and superheated.
- Time: Time itself can stretch in unusual ways near a black hole.
- Planets: Black holes can cause mass loss in planetary atmospheres. They can also strip apart binary star systems, accelerating one star and capturing the other.
- Earth: A black hole hitting Earth would create a shockwave that would produce seismic waves across the planet. Even a black hole with the lowest possible mass would produce an earthquake with a magnitude of 4. According to Fox Weather, no black hole is close enough to Earth to be a danger.
Here are some facts about black holes:
- Size Black holes come in a range of sizes, from the size of an atom to the size of a mountain. The most common type of black hole is the stellar black hole, which can be up to 20 times the mass of the sun.
- Hawking radiation Black holes emit radiation over time, which disperses their mass into space. This process is known as Hawking radiation, or black hole evaporation.
- Time dilation According to Einstein’s theory of general relativity, time slows down near a black hole. This is known as “gravitational time dilation”.
- Space and time Black holes distort time and space around them.
- Primordial black holes These are the smallest type of black hole, ranging in size from the size of an atom to the mass of a mountain. Here are some other facts about black holes:
- You can’t directly see a black hole.
- The Milky Way likely has a black hole.
- There are likely millions of black holes in our galaxy.
- If you fell into a black hole, you would never escape.
- A black hole could fit in your pocket.
a black hole in a galaxy can spit out material at high speeds, clearing out its neighborhood.
Black holes are known to “burp” after eating stars, spitting out material back into space months or years later. Researchers call these latent bursts of energy “burps” because of the delay between consumption and regurgitation.
In 2022, Harvard Cendes reported that a black hole began burping out material from a star it ate years ago. The material is traveling as fast as 50 percent the speed of light. The researchers are unsure why this outflow was delayed by several years.
Their overwhelming gravity draws material toward them, where it collects in an accretion disk, waiting its turn to cross the event horizon into oblivion. But in one galaxy, the SMBH has choked on its meal and spit it out, sending material away at high speeds and clearing out the entire neighbourhood
Some scientists believe the material ejected from black holes are cosmic rays, which are some of the fastest-traveling particles in the universe.
Black holes are surrounded by a hot, swirling matter called an accretion disk. This disk is made up of gas and dust that collects, swirls, and flattens into a pancake shape. Some scientists believe that as the black hole swallows up nearby gas and dust, a small portion of the material is ejected due to the rapid rotation and magnetic field of the accumulated gas.
Scientists also believe that the stream of gas gets whipped around a black hole during these events, colliding with itself. This is thought to create shock waves and outward flows of gas that generate visible light, as well as wavelengths not visible to the human eye, such as ultraviolet light and X-rays
Please like subscribe comment your precious thoughts on universe discoveries
Full article source google
Best headphones on great discount on Amazon