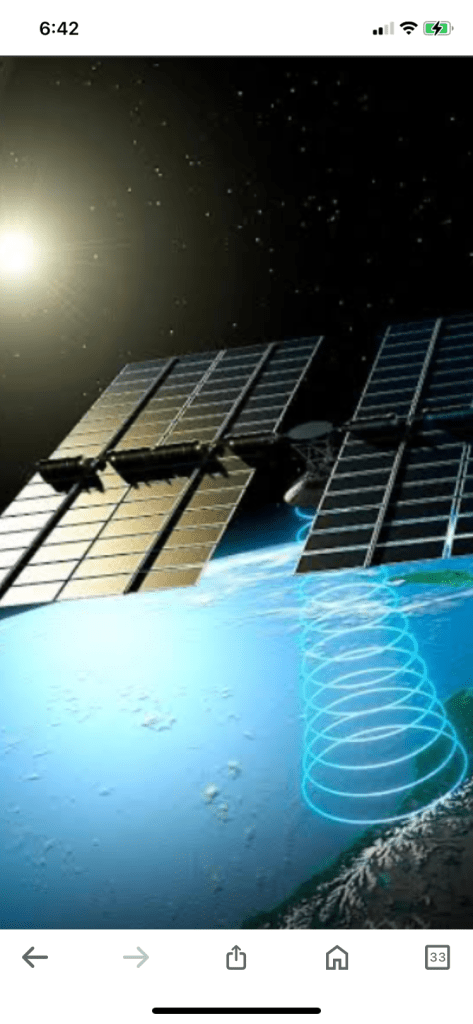
The Space Solar Power Demonstrator (SSPD-1) is a prototype from Caltech’s Space Solar Power Project (SSPP). The SSPD-1’s MAPLE experiment can wirelessly transfer collected solar power to receivers in space.
Space-based solar power involves harvesting solar energy in space and beaming it to Earth. This concept aims to:
- Provide continuous base-load energy
- Use less land than conventional renewables
- Overcome the intermittency of terrestrial renewable energy Space-based solar power involves:
- Using energy transmitting satellites with solar panels
- Using giant mirrors to reflect solar rays onto smaller solar collectors
- Wirelessly beaming the radiation to Earth as a microwave or laser beam
Space-based solar power (SBSP) works by converting sunlight into another form of energy, like microwaves, and transmitting it to Earth.
Here’s how it works:
- Solar panels: Satellite photovoltaic panels convert the sun’s energy into electromagnetic waves at microwave frequencies.
- Microwave beam: The satellite beams the microwave energy to a receiver on Earth.
- Direct current: The receiver transforms the microwave energy into direct current. SBSP has the potential to revolutionize clean energy production. Solar energy is more intense and uninterrupted by Earth’s atmospheric conditions in space, which means SBSP can provide a steady and robust energy supply.
Space-based solar power has several advantages over Earth-based solar power:
- Continuous power Space-based solar power stations are illuminated by the sun 24 hours a day, allowing for continuous electricity generation. Earth-based solar power systems can only produce electricity during the day and are dependent on the weather.
- Higher energy collection Space-based solar power systems can collect more energy due to the lack of reflection and absorption by the atmosphere. Solar panels in orbit can generate about twice as much power as the equivalent panel on Earth.
- Higher efficiency Space-based solar panels can be around 34% efficient, while most commercial solar panels can only reach 15-20% efficiency.
- Zero terrestrial environmental impact Space solar power would have essentially zero terrestrial environmental impact due to materials extraction from the Moon or near-Earth asteroids, and space-based manufacture of components.
Here are some differences between space solar and ground solar:
- Energy collection Space-based solar panels can collect more energy due to the lack of reflection and absorption by the atmosphere. According to Caltech, space-based solar panels can generate up to eight times as much electricity as land-based solar panels.
- Efficiency Space-based solar panels can be around 34% efficient, while most commercial solar panels can only reach 15-20% efficiency.
- Accessibility Ground-mounted solar panels are easily accessible, making maintenance easier.
- Cooling Ground-mounted solar systems are usually cooler than those installed on a roof. With less heat, there’s less friction as the solar energy transfers from the panels to your electrical system.
- Sun exposure Ground-mounted solar panels offer optimal sun exposure. Some ground-mount solar panel systems can move with the sun in order to capture the most sunlight they can each day.
With humanity rapidly using up Earth’s fossil fuel reserves, turning to the heavens for our energy needs appears inevitable. The futuristic vision of microwave power plants beaming energy from space, once relegated to the realm of science fiction, has just taken a monumental step toward reality
Unlike here on Earth, solar energy in space is unencumbered by factors like day and night, or obstruction by clouds and weather on our planet. This makes space-based solar harvesters ideal as they could potentially yield roughly eight times more power than even the most efficient solar panels on the Earth’s surface
In June 2023, scientists beamed solar power to Earth from space for the first time. The Space Solar Power Demonstrator (SSPD)’s Microwave Array for Power-transfer Low-orbit Experiment (MAPLE) used a satellite called DOLCE to beam 100 milliwatts of power.
Space-based solar power (SBSP) is the concept of collecting solar power in space and distributing it to Earth. The benefits of SBSP include:
- Clean, continuous base-load energy
- Much lower land usage than conventional renewables
- Higher collection of energy due to the lack of reflection and absorption by the atmosphere The basic premise of SBSP technology is that photovoltaic panels on a satellite in space convert the sun’s energy to electromagnetic waves at microwave frequencies. The satellite then beams the microwave energy to a receiver on Earth that transforms it into direct current.
Please like subscribe comment your precious thoughts on universe discoveries
Full article source google
Best travel products on heavy discount on Amazon