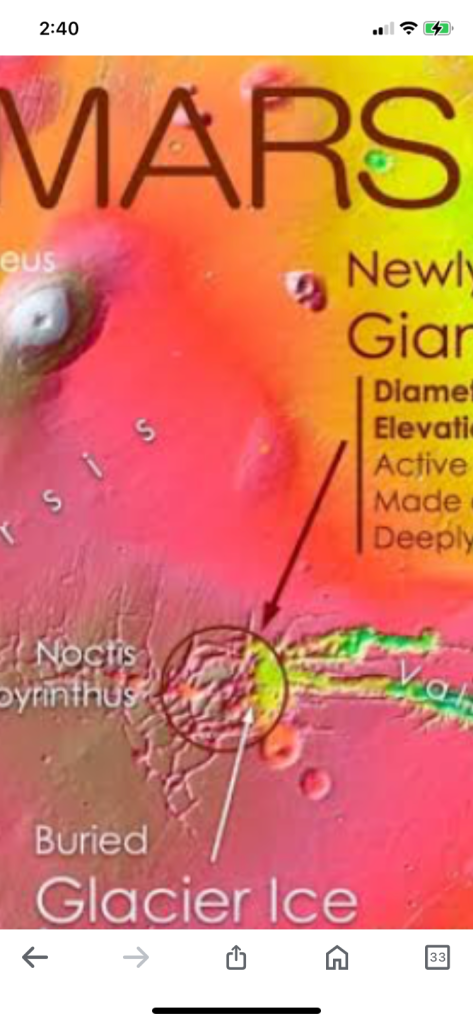
In March 2024, scientists announced the discovery of a giant volcano on Mars that had been hidden for decades. The volcano, temporarily named Noctis, is 280 miles wide and is located at the boundary of the Noctis Labyrinthus and Valles Marineris
The volcano is a shield volcano made up of layers of lava, ice, and pyroclastic material. The ice has built up over time from snow and ice accumulation on the volcano’s flanks. The volcano’s location on the eastern edge of Tharsis, a broad regional topographic rise, makes it a prime location for searching for life on Mars
Scientists have discovered a giant volcano on Mars that has been “hidden in plain sight” for more than 50 years. The volcano is around 280 miles (450 kilometers) wide and more than 29,600 feet (9,000 meters) high
Mars has fewer than 20 named volcanoes, and only five of those are giant shields. The main cluster of volcanoes and lavas is in Tharsis, with a smaller cluster of three volcanoes in Elysium
Mars also has a wide range of other volcanic features, including large volcanic cones, unusual patera structures, and mare-like volcanic plains.
Mars doesn’t have tectonic plates that move over hotspots, like in Hawaii. Instead, it can build one huge volcano. Mars’ lower gravity also allows magma to be pushed to great heights.
Mars volcanoes don’t appear active. However, scientists have confirmed that a region of northern Mars called Arabia Terra experienced thousands of massive volcanic eruptions over a 500-million-year period. These eruptions are known as “super eruptions” and are the largest known volcanic eruptions.
Olympus Mons is the largest volcano in the solar system and the highest point on Mars. It’s a shield volcano that’s 25 kilometers (16 miles) high and 624 kilometers (374 miles) in diameter. That’s about the size of Arizona
Olympus Mons is located in the Tharsis Montes region of Mars, where volcanoes are 10 to 100 times larger than those on Earth. The lava flows on Mars are also much longer
Mars has a lot of volcanic features, including lava plains, lava flows, and the largest volcanoes in the solar system. However, there is no volcanic activity on Mars today. Mars’ interior cooled and solidified a billion years ago
However, in late October 2022, researchers announced evidence that Mars is still volcanically active below its surface. The researchers analyzed seismic signals from marsquakes and found that molten lava, or magma, still exists underground. The researchers say that vulcanism still plays an active role in shaping the Martian surface.
Mars has seen a lot of volcanic activity in the past, and has more volcano-related rocks and features than Earth. Large-scale volcanism on Mars started before the planet was even a billion years old and was active for roughly a billion years thereafter.
Mars’ volcanoes are so tall because the planet lacks tectonic plates, which means the crust above a volcanic fissure doesn’t move. This allows lava to build up over time, resulting in larger volcanoes. Mars’ lower surface gravity, about 38% of Earth’s, also allows volcanic materials to be ejected higher into the atmosphere
The lower gravity on Mars also helps push the magma. The crust of Mars remains fixed over a stationary hotspot, and a volcano can continue to discharge lava until it reaches an enormous height.
Other factors that affect the size of volcanoes include: the minerals in the magma, the viscosity of the molten rock, the amount of magma in the magma chamber, and the pressure within the chamber.
The higher the pressure, the greater the force of the eruption, and the higher the ejected material can go, the taller a volcano can be
In March 2024, scientists announced the discovery of a giant volcano on Mars that had been hidden for decades. The volcano, temporarily named Noctis, is 280 miles wide and is located at the boundary of the Noctis Labyrinthus and Valles Marineris
The volcano is a shield volcano made up of layers of lava, ice, and pyroclastic material. The ice has built up over time from snow and ice accumulation on the volcano’s flanks. The volcano’s location on the eastern edge of Tharsis, a broad regional topographic rise, makes it a prime location for searching for life on Mars
Please like subscribe comment your precious thoughts on universe discoveries
Full article source google
https://www.amazon.in/b?_encoding=UTF8&tag=555101-21&linkCode=ur2&linkId=297f43a202fd21cae0cefd214e486472&camp=3638&creative=24630&node=1984443031