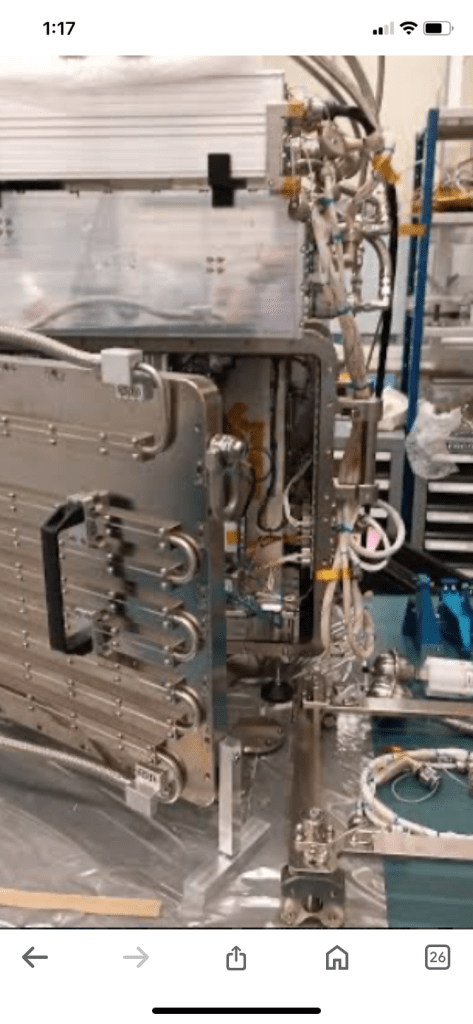
The first metal 3D printer aboard the International Space Station successfully dribbled out a molten “S curve” last Thursday, in what the European Space Agency (ESA) is calling a “giant leap forward for in-orbit manufacturing.”
Combining a high-power laser and stainless-steel wire, an Airbus-built metal 3D printer deposited its first liquefied test lines inside the ESA’s Columbus research module.
For “safety reasons,” the machine operated in a “fully sealed box, preventing excess heat or fumes from escaping,” the agencywrote, adding that the laser on the printer is “about a million times more powerful than a standard laser pointer.” Microgravity researchers at the French space agency CNES oversaw the project remotely from facilities in Toulouse, alongside Airbus and the ESA.
What is metal 3D printing?
One of the most common metal 3D printing methods is the Powder Bed or Powder Bed Fusion process. The various types of Powder Bed Fusion typically use heat or light energy, in the form of a laser or electron beam, to fuse or melt metal powder material together – and involve spreading the material over previous layers.
Can you 3D print metal materials?
While 3D printers can be used to produce parts out of common metals such as steel, they can also fabricate parts out of superalloys that are uniquely suited for extreme environments
What is the metal print technique?
In a nutshell, the metal print is a dye sublimation process where the ink is infused into a special coating on the metal which produces a glossy and vibrant end result if using the high gloss Chromaluxe product
Are metal 3D printers safe?
Metal 3D printer filament consisting of bound powder is relatively safe to use, and machines can be used effectively with minimal training and PPE
Where is metal 3D printing used?
The metal 3D printing process involves sintering or melting metal powders directly, or combining them with a second material to allow delivery through a nozzle. It is used for both rapid prototyping and finished production parts for aerospace, mechanical engineering, tooling and more
How expensive is metal 3D printing?
How much does metal 3d printing really cost? You’re looking somewhere between $15 per piece up to $800 for larger models. Similar to the cost of 3d printing service, metal 3d printing depends on factors such as the volume of your 3d model, complexity and the type of finishing that you use, in this case metal
What is the raw material for metal 3D printing?
Popular Metal 3D Printing Materials
Stainless steel has high strength, high ductility, and is resistant to corrosion. Aluminum is a lightweight, durable, strong, and has good thermal properties. Tool steel is a hard, scratch-resistant material that you can use to print end-use tools and other high-strength parts..
Which metal is best for 3D printing?
Steel is the most common metal used in 3D printing. Its excellent material properties, versatility, and broad use in precision manufacturing make 3D printing steel an excellent option for creating high quality parts.
Is metal 3D printing the future?
According to Grand View market research reports, the global metal additive market was valued at $7.73 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 24.6% from 2024 to 2030
What are 3D printers used for in space?
There are already several plastic 3D printers on board the International Space Station (ISS), the first of which arrived in 2014. Astronauts have already used them to replace or repair plastic parts, since one of the major problems of everyday life in space is the supply of equipment, which can take months to arrive
An operational version of this metal 3D printer would eliminate the need to send a tool up with a rocket and allow the astronauts to print the needed parts in orbit
The Metal 3D Printer’s design is based on stainless-steel wire being fed into the printing area, which is heated by a high-power laser, about a million times more powerful than a standard laser pointer. As the wire dips into the melt pool, the end of the wire melts so that metal is added to the print.
The print process is overseen entirely from the ground. All the onboard crew has to do is open a nitrogen and venting valve before the printing starts. For safety reasons the printer operates within a fully sealed box, preventing excess heat or fumes from escaping.
One of ESA’s goals for future development is to create a circular space economy and recycle materials in orbit to allow for a better use of resources, such as repurposing bits from old satellites into new tools or structures. An operational version of this metal 3D printer would eliminate the need to send a tool up with a rocket and allow the astronauts to print the needed parts in orbit.
What are the applications for 3D printing in space?
3D Printing is Used to Make Satellites
Additive manufacturing is also increasingly being used in space is for satellites. Currently, there are projects from a number of companies including Boeing and Airbus which have used additive manufacturing to create increasingly complex, lighter parts for their satellites
Metal 3D printing makes life easier for astronautsThis logistical constraint will intensify on future Moon and Mars stations in the next few decades. Even though the raw material still needs to be launched, printing the part is still more efficient than transporting it whole up to its final destination
Building a lunar base with 3D printing
Setting up a lunar base could be made much simpler by using a 3D printer to build it from local materials. Industrial partners including renowned architects Foster + Partners have joined with ESA to test the feasibility of 3D printing using lunar soil.
This new 3D printer printing metal parts represents a world first, at a time of growing interest in in-space manufacturing,” explains ESA technical officer Rob Postema. “Polymer-based 3D printers have already been launched to, and used aboard the ISS, using plastic material that is heated at the printer’s head, then deposited to build up the desired object, one layer at a time
Metal 3D printing represents a greater technical challenge, involving much higher temperatures and metal being melted using a laser. With this, the safety of the crew and the Station itself have to be ensured – while maintenance possibilities are also very limited. If successful though, the strength, conductivity and rigidity of metal would take the potential of in-space 3D printing to new heights.”
What is the strongest type of metal 3D printing?
The Best Metal 3D Printing Materials for Additive Manufacturing
- Stainless Steel. Stainless steel is characterized by high strength and excellent corrosion resistance. …
- Tool Steels. As the name suggests, this class of steels is used for a variety of manufacturing tooling. …
- Titanium. …
- Inconel 625. …
- Copper
3d printing in space travel
3D printing is an experimental technology that could revolutionize space exploration. It has many potential uses, including:
- Manufacturing spare parts Astronauts can use 3D printers to create spare parts, tools, and other components on demand. This can be especially helpful since equipment supplies can take months to arrive in space. For example, NASA and Made in Space have collaborated to create a zero-gravity 3D printer that can print plastic objects using Fused Filament Fabrication technology.
- Researching and manufacturing goods The vacuum and zero-gravity environment of space could allow companies to research and manufacture goods that are not possible on Earth. For example, 3D printing could be used to create hollow objects like heart valves, and to print human organs that can withstand gravity when returned to Earth.
- Producing food 3D printing could be used to create cell-based meat with the same texture, flavor, and structure as a traditional steak.
The International Space Station (ISS) has had plastic 3D printers on board since 2014, and in January 2024, Airbus announced that the world’s first metal 3D printer for space was on its way to the ISS. NASA has also been using 3D printing since the late 1990s, and in the 2010s began developing components for liquid rocket engines using additive manufacturing
Please like subscribe comment your precious thoughts on universe discoveries
Full article source google
https://www.amazon.in/b?_encoding=UTF8&tag=555101-21&link
Stunning what we’re ‘printing’ now.
LikeLike
So beautiful article with details about this 💥
LikeLike
Great article, the future is made by 3d printing!
LikeLiked by 1 person