ISRO Aditya L1 Mission ISRO’s first solar mission Aditya L1 has achieved significant success. The spacecraft has captured and sent back images of many of the Sun’s recent activities. ISRO said that these pictures have been taken with the help of two remote sensing instruments installed in the spacecraft. ISRO has shared many pictures of different solar flares.
PTI, Bengaluru. ISRO Aditya L1 Mission: ISRO’s first solar mission Aditya L1 has achieved significant success. The spacecraft has captured and sent back images of many of the Sun’s recent activities. ISRO said that these pictures have been taken with the help of two remote sensing instruments installed in the spacecraft.
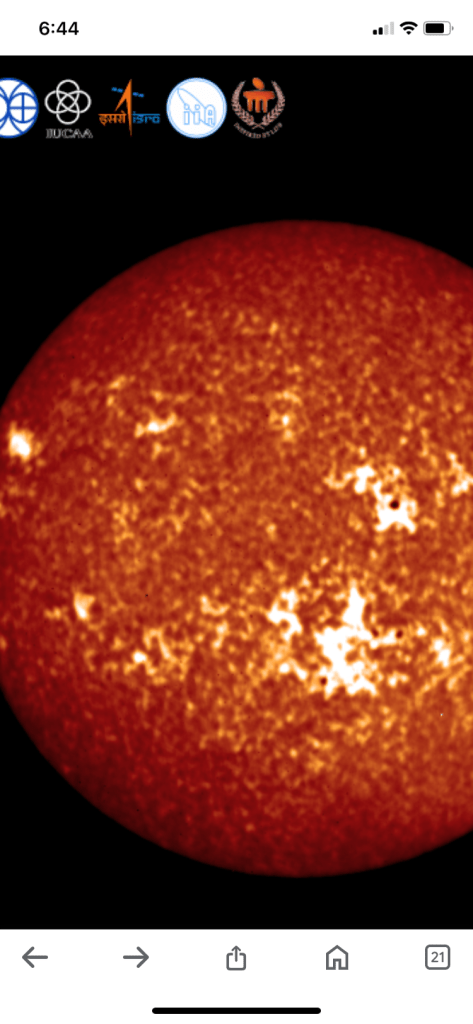
इसरो ने अलग-अलग सोलर फ्लेयर्स की कई तस्वीरें साझा की हैं, जोकि मई 2024 के दौरान ली गई हैं। इसरो के अनुसार सोलर अल्ट्रा वायलेट इमेजिंग टेलीस्कोप (SUIT) और विजिबल एमिशन लाइन कोरोनाग्राफ (VELC) सेंसर ने ये गतिविधियां कैद की।
क्या कहा इसरो ने
इसरो ने अपने बयान में कहा कि कोरोनल मास इजेक्शन (सीएमई) से जुड़ी कई एक्स-क्लास और एम-क्लास फ्लेयर्स दर्ज की गईं, जिससे महत्वपूर्ण भू-चुंबकीय तूफान पैदा हुए। स्पेस एजेंसी ने कहा कि सूर्य के AR13664 सक्रिय क्षेत्र में 8 से 15 मई के दौरान कई एक्स-श्रेणी और एम-श्रेणी की ज्वालाएं फूटीं, जो 8 और 9 मई के सीएमई से जुड़ी थीं। इनसे 11 मई को एक बड़ा भू-चुंबकीय तूफान पैदा हुआ।
ISRO has shared several pictures of different solar flares, which were taken during May 2024. According to ISRO, the Solar Ultra Violet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) and Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC) sensors captured these activities.
What did ISRO say?
ISRO said in its statement that several X-class and M-class flares associated with coronal mass ejections (CMEs) were recorded, causing significant geomagnetic storms. The space agency said several These created a major geomagnetic storm on May 11.
गौरतलब है कि आदित्य-एल1 भारत का पहला सौर मिशन है, जोकि दो सितंबर, 2023 को लॉन्च हुआ था। लॉन्च होने के 127 दिन बाद इस साल छह जनवरी को यह लैग्रेंजियन बिंदु (एल1) पर पहुंचा। एल1 पृथ्वी से लगभग 1.5 मिलियन किमी दूरी पर स्थित है। यहां से अंतरिक्ष यान लगातार सूर्य को देखने में सक्षम है।
It is noteworthy that Aditya-L1 is India’s first solar mission, which was launched on September 2, 2023. It reached the Lagrangian point (L1) on January 6 this year, 127 days after its launch. L1 is located at a distance of about 1.5 million km from Earth. From here the spacecraft is able to observe the Sun continuously.
Yes, ISRO’s Aditya-L1 mission has achieved several successes in its solar mission, including capturing full-disk images of the sun and images of solar activity:
- Full-disk images In December 2023, ISRO shared the first-ever full-disk images of the sun in near ultraviolet wavelengths, taken by the Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) on board Aditya-L1. The images were taken using 11 different filters across various wavelengths, and provide insights into the sun’s photosphere and chromosphere. ISRO says these images mark a significant step in understanding the sun’s dynamic features and showcase India’s technological progress.
- Solar activity In June 2024, ISRO shared images of solar activity captured by Aditya-L1 during a solar storm in May 2024. The images were taken by SUIT and the Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC) sensor, and show several X-class and M-class flares that erupted in the active region AR13664 on the sun
Aditya-L1 launched from the Satish Dhawan Space Center in Sriharikota on September 2, 2023, and is India’s first space-based solar observatory. Nigar Shaji, a scientist at the UR Rao Satellite Centre in Bengaluru, is the project director for Aditya-L1
Two of the remote sensing payloads on board India’s maiden solar mission Aditya-L1 have captured images of the Sun and its dynamic activities during the solar storm, which occurred during the month of May. Between May 8 and 15, several X-class and M-class flares erupted in the active region AR13664 on the Sun
What are the achievements of Aditya-L1?
Aditya-L1, following a flight duration of 63 minutes and 20 seconds, achieved a successful injection into an elliptical orbit around the Earth at 12:54 IST. Aditya-L1 underwent a series of four Earth-bound orbital maneuvres prior to its injection to a transfer orbit towards the Lagrange point (L1
Will Aditya-L1 return to Earth?
“Aditya-L1 will stay approximately 1.5 million km away from Earth, directed towards the Sun, which is about 1 per cent of the Earth-Sun distance. The Sun is a giant sphere of gas and Aditya-L1 would study the outer atmosphere of the Sun
What are the important facts about Aditya-L1?
Quick Facts: Aditya-L1 will stay approximately 1.5 million km away from Earth, directed towards the Sun, which is about 1% of the Earth-Sun distance. The Sun is a giant sphere of gas and Aditya-L1 would study the outer atmosphere of the Sun. Aditya-L1 will neither land on the Sun nor approach the Sun any closer
What are the benefits of Aditya-L1 mission?
The suit of Aditya L1 payloads are expected to provide most crucial information to understand the problems of coronal heating, Coronal Mass Ejection, pre-flare and flare activities, and their characteristics, dynamics of space weather, study of the propagation of particles, and fields in the interplanetary medium etc
What technology is used in Aditya-L1?
The Aditya-L1 spacecraft is outfitted with various sensors and instruments, including a solar ultraviolet imaging telescope, a high-energy X-ray spectrometer, and a magnetometer. These sensors and instruments gather critical data concerning the Sun’s atmosphere, magnetic field, and solar wind
What is the mission of Aditya-L1 for kids?
Understanding the Sun: The Aditya-L1 mission focuses on studying the Sun, our closest star. Teaching kids about the Sun’s role in the solar system, its structure, and its impact on Earth’s environment helps build a foundation for understanding celestial bodies and space phenomena
Who is the scientist of Aditya-L1?
Sankarasubramanian K.
Sankarasubramanian K. is a senior solar scientist at the U R Rao Satellite Centre (URSC) in Bengaluru, India. He has been appointed as the Principal Scientist of ISRO’s Aditya-L1 mission, which is a solar mission that will study the Sun’s atmosphere and its impact on the Earth’s climate
Which rocket is used in Aditya-L1?
The Aditya-L1 mission will be launched by ISRO’s PSLV XL rocket from Satish Dhawan Space Centre SHAR (SDSC-SHAR), Sriharikota
What is the cost of Aditya-L1?
5.5 crores USD (2018)Aditya-L1/Cost
What is the next mission of ISRO after Aditya-L1?
After success of ‘Chandrayaan-3’and ‘Aditya-L1’, ISRO sets eyes on ‘Gaganyaan-1‘ mission. In a remarkable succession following the triumphs of ‘Chandrayaan-3’ and ‘Aditya-L1’ missions, ISRO is gearing up for ‘Gaganyaan
Which material is used in Aditya-L1?
The launcher was built with MIDHANI’s materials like Ti-6Al-4V Titanium alloy – PS4 Tank and Gas bottles, C-103 Niobium Alloy – PS4 thrust chamber, Superco 605 Cobalt Alloy – PS2 thrust chamber, Ultra High Strength Steel – Motor Case & 15CDv6 – strap on motor case and base rings, the release further stated
Please like subscribe comment your precious thoughts on universe discoveries
Full article source google
