Fastest Spinning Star In The Universe: The fastest spinning white dwarf star in the universe completes one revolution in just 13 seconds. This star, known as ‘Vampire Star’ or ‘Vampire Star’, is shrinking rapidly and will soon explode
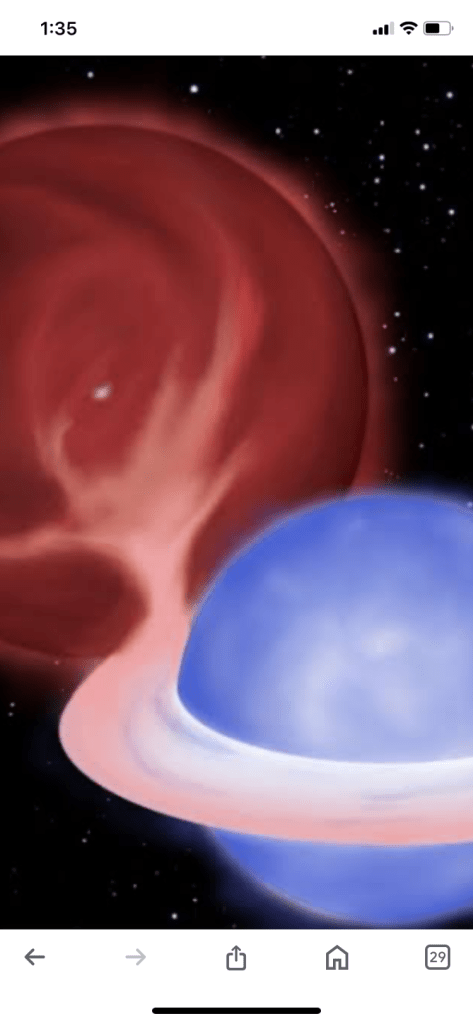
There is a star in this universe which is continuously getting heavier. It is shrinking and rotating rapidly, stealing material from its companion star. This star is a ‘white dwarf’ named RX J0648.0–4418. Scientists call it a ‘cosmic vampire’. This white dwarf is getting ready to turn into a supernova one day by stealing material from its companion star.
RX J0648.0–4418 is a companion star to HD 49798, 1,700 light-years away from Earth. Its mass is about 1.2 times the mass of our Sun, and it rotates just once every 13 seconds. This is the fastest rotating white dwarf ever seen. In comparison, the second fastest white dwarf, LAMOST J0240+1952, rotates every 25 seconds.
Why does this ‘vampire star’ rotate so fast?
RX J0648.0–4418’s fast spin cannot be explained solely by material stolen from its companion star. A new study found that the reason for this could be its gradual shrinkage. This process is just like an ice skater putting his hands inside and starts spinning rapidly
Sandro Merighetti, the scientist leading the research, said, ‘The white dwarf gradually shrinks during the first few million years of its life, which increases the speed of its rotation.’ RX J0648.0–4418’s young age (only a few million years) makes it different from other white dwarf systems, which are typically billions of years old. His research has been published on arXiv.
The white dwarf emits X-ray light and is sucking material from its companion star, which is a hot helium-burning subdwarf. Such a binary system is the only known example of its kind.
The mass of RX J0648.0–4418 is close to the ‘Chandrasekhar limit’ (1.4 solar masses). This is the limit beyond which the white dwarf turns supernova. At the moment, this star is sucking material from its companion, and as its companion star evolves, this process will become faster. Scientists estimate that this white dwarf will turn into a supernova within the next 100,000 years
RX J0648.0-4418: A Shrinking White Dwarf Star
RX J0648.0-4418 is a unique binary star system located approximately 1,700 light-years away from Earth. It consists of a white dwarf star and a hot subdwarf star. The white dwarf, the primary focus of interest, is rapidly spinning and accreting matter from its companion star.
Key Characteristics:

- Rapid Rotation: The white dwarf spins at an astonishing rate, completing a full rotation every 13 seconds. This makes it one of the fastest-spinning white dwarfs known.
- Shrinking Size: As the white dwarf accretes more matter, it’s actually shrinking in size rather than expanding. This is a rare phenomenon and is thought to be due to the star’s rapid rotation.
- Approaching Chandrasekhar Limit: The white dwarf is gaining mass and is approaching the Chandrasekhar limit, a critical mass beyond which a supernova explosion becomes inevitable.
- Potential Supernova: Scientists predict that RX J0648.0-4418 may undergo a supernova explosion in about 100,000 years.
Why is it important?
RX J0648.0-4418 provides a unique opportunity to study the evolution of binary star systems and the behavior of white dwarfs near the Chandrasekhar limit. By observing this system, astronomers can gain valuable insights into the processes that lead to supernova explosions.
vampire stars
Vampire Stars: Cosmic Cannibals
Vampire stars, also known as blue straggler stars, are a peculiar type of star found in star clusters. They are called “vampire stars” because they defy the normal process of stellar evolution by siphoning off material from their companion stars. This stolen material rejuvenates the vampire star, making it appear younger and more massive than it should be based on its age.
How do vampire stars work?
- Binary Star Systems: Vampire stars typically exist in binary systems, where two stars orbit each other.
- Mass Transfer: Through a process called mass transfer, one star (the vampire star) gradually siphons off material from its companion star. This can happen through a variety of mechanisms, such as stellar winds or Roche lobe overflow.
- Rejuvenation: The stolen material increases the vampire star’s mass, causing it to become hotter and brighter. This rejuvenation process can significantly extend the star’s lifespan.
Why are vampire stars important? - Stellar Evolution: Vampire stars challenge our understanding of stellar evolution, as they don’t follow the typical path of aging and dying.
- Star Cluster Dynamics: Studying vampire stars can provide insights into the dynamics of star clusters, including how stars interact and evolve within these dense environments.
- Formation of Heavy Elements: The mass transfer process in vampire star systems can lead to the formation of heavy elements, which are essential for the creation of planets and life.
Please like subscribe comment your precious comment on universe discoveries
sk-mania-blogs.in
Full article source google
https://www.buymeacoffee.com/Satyam55
If you like my website universe discoveries please donate me a coffee freinds

🙏🌹
Aum Shanti
LikeLike