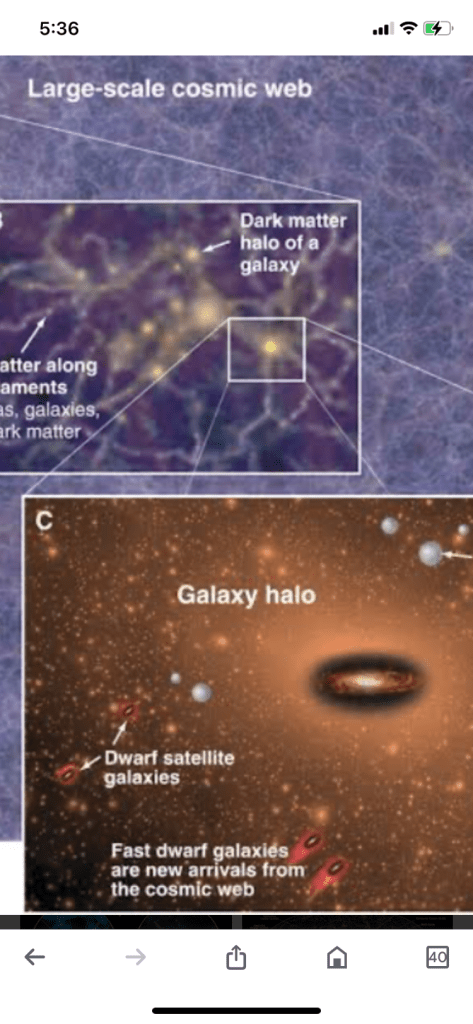
What is the cosmic web of the galaxy
Accordingly to cosmological simulations, over 60% of the hydrogen that was created by the Big Bang roughly 13.8 billion years ago collapsed to form a sheet, which then broke apart to make the web of cosmic filaments we see today. These filaments connect galaxies and feed them gas for growth and star formation
What is the web theory of the universe
J . Richard Gott was among the first cosmologists to propose that the structure of our universe is like a sponge made up of clusters of galaxies intricately connected by filaments of galaxies—a magnificent structure now called the “cosmic web” and mapped extensively by teams of astronomers
How did we see the cosmic web
The Feeble Glow of Filaments
The best way to see the cosmic web directly is to pick up signatures of its main component, hydrogen gas, using instruments called spectrometers, which spread light out into a multitude of wavelengths, also known as a spectrum
What is the biggest thing in the cosmic web
Galactic Walls
These walls are likely the largest-known superstructures within the observable universe. They can stretch hundreds of millions of light-years across but are relatively thin – only about 20 million light-years deep
Who hold the cosmic web
During the further evolution, gravity holds galaxies, clusters and filaments together and maps the Cosmic Web into its present shape
Does the cosmic web move
they found that these long tendrils of galaxies and matter, forming the vast cosmic filaments of the cosmic web, rotate on the scale of hundreds of millions
Where is earth in the cosmic web
Well, Earth is located in the universe in the Virgo Supercluster of galaxies. A supercluster is a group of galaxies held together by gravity. Within this supercluster we are in a smaller group of galaxies called the Local Group. Earth is in the second largest galaxy of the Local Group – a galaxy called the Milky Way
What does this cosmic web look like
Between these clusters, galaxies align along thin threads, the “galactic filaments”, which can be several hundred million light-years long. Galactic clusters and filaments are surrounded by voids that contain very little matter. Altogether, the cosmic web looks somewhat like a human brain
What is the difference between universe and cosmic web
The universe isn’t a random jumble of objects; it has a structure composed of galaxies and gas. Cosmologists call this structure the cosmic web. The cosmic web is composed of interconnecting filaments of clustered galaxies and gases stretched out across the universe and separated by giant voids
Who discovered the cosmic web
J . Richard Gott was among the first cosmologists to propose that the structure of our universe is like a sponge made up of clusters of galaxies intricately connected by filaments of galaxies—a magnificent structure now called the “cosmic web” and mapped extensively by teams of astronomers
Best clothes for men on women on huge discount on Amazon
https://ee78eenj92-vhq90too7q52way.hop.clickbank.net
awesome post, thanks for sharing!
LikeLike