A kilonova is a huge explosion that occurs when two neutron stars or a neutron star and a black hole collide. These events are extremely energetic, and can release as much energy in a few seconds as our Sun will produce in its entire 10-billion-year lifetime.
Kilonovas are bursts of electromagnetic radiation that result from the radioactive decay of iron atoms in material ejected when two neutron stars smash together or when a neutron star merges with a black hole. They release heavy metals like gold, silver, and selenium into outer space at tremendous velocities, as well as radiation.
Kilonovas are believed to be a significant source of the universe’s heavy elements. They appear to be very rare events. Scientists believe that only ten star systems that exist in the Milky Way will end in kilonovae.
Kilonovas can result in the formation of a new neutron star or black hole. They also emit gravitational waves and wide-band electromagnetic emission (gamma, X, optics, IR, radio).
Kilonovas are 1,000 times brighter than a nova, but only 1/10th to 1/100th as bright as a supernova. However, kilonovas eject matter at a faster speed than supernovas, at 30-60,000 km/s compared to 10,000 km/s. Kilonovas also emit more energy in the form of gravitational waves.
At their peak, supernovas can be brighter than an entire galaxy and can reach a diameter of several light-years across.
Is a kilonova a type of supernova
No, a kilonova is not a type of supernova. A supernova is the explosive death of a massive star when it runs out of fuel for nuclear fusion. A kilonova is a similar cosmic event that occurs when two neutron stars or a neutron star and a black hole collide.
Kilonovas are different from both a standard nova and a supernova. They are more energetic than a typical nova, but less bright than a classic supernova. They were originally called mini-supernovas because they are 1/10 to 1/100 the brightness of a typical supernova
A kilonova is also called a macronova. It’s a fast-evolving, supernova-like phenomenon that occurs when two neutron stars or a neutron star and a black hole merge. Kilonovas are also known as:
- Core collapse” supernovas
- Hypernovas
- Unnovas
A kilonova can result in the formation of a black hole. The final result of a kilonova is a “hypermassive” neutron star that rapidly collapses to form a black hole.
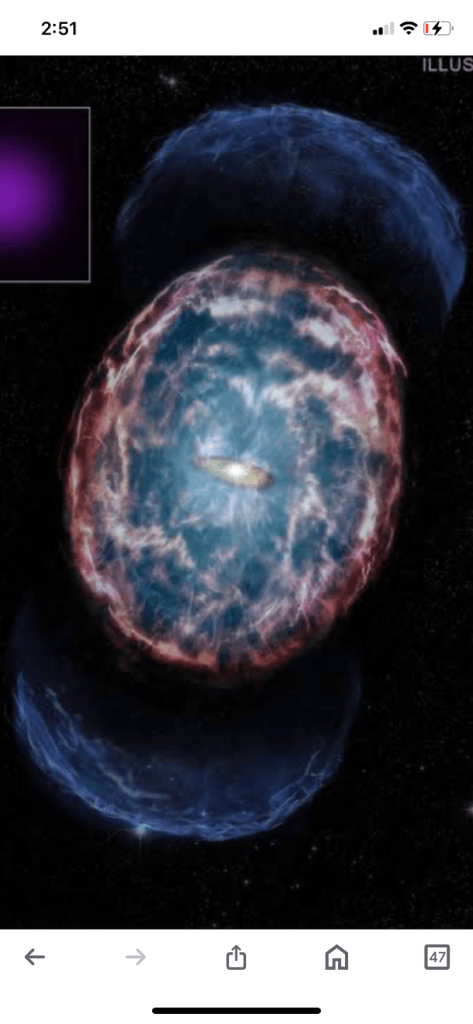
Astronomers have observed two neutron stars merging to form a black hole. The collision occurred in a galaxy about 140 million light-years away. The stars merged and collapsed to form a black hole, while throwing out fragments that produced a perfectly spherical fireball of blue and red
Kilonovas are typically about 20 kilometers across, but can weigh one and a half to two times as much as the Sun. They are completely symmetrical, almost perfect spheres.
Astrophysicists were surprised to discover that kilonovas are spherical. “No one expected the explosion to look like this. It makes no sense that it is spherical, like a ball”.
Kilonovas are hot, highly radioactive material that expands and thins enough for infrared light to escape. At its peak brightness, the explosion is about a thousand times brighter than a classical nova.
Yes, astronomers have observed kilonovas:
- In October 2017, astronomers observed the first confirmed kilonova after two neutron stars collided.
- In November 2020, scientists observed the brightest kilonova candidate ever discovered.
- In February 2022, astronomers led by Northwestern University may have detected the afterglow of a kilonova.
- In December 2021, astronomers observed a kilonova emission while tracing a burst of high-energy light from the Milky Way.
Astronomers usually spot kilonovas after they’ve merged and emitted powerful gamma-ray bursts (GRBs).
Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are the most powerful explosions in the universe. Hypernovas are similar to supernovas, but can be 10 to 100 times more powerful. Hypernovas occur when stars with more than 30 solar masses undergo core collapse
Kilonovas are extremely rare. Astronomers believe that there are only about 10 kilonova progenitor systems in the Milky Way. One of these systems is CPD-29 2176, which was discovered by NASA’s Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory.
Kilonovas are rare for a few reasons:
- Only a small percentage of stars are the right size to become neutron stars.
- Many supernova explosions kick companion stars away so powerfully that they end up shooting across the galaxy, sometimes escaping entirely.
Kilonovas are so rare that one astronomer called the progenitor system a “one-in-ten-billion” observation
Best watches on discount on Amazon
https://5155eihe4y1xcyfp0gie6wi1em.hop.clickbank.net
You are knowledge personified 😊
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thanks sir I research a lot on universe my favourite subject
LikeLiked by 1 person