The CosmicFlows data suggest that we could be part of the Shapley Concentration, which could be 10 times the volume of Laniakea. It’s about half the volume of the largest structure in space, known as “the Great Wall”, which is a string of galaxies stretching across 1.4 billion light-years
If you want to pinpoint your place in the Universe, start with your cosmic address. You live on Earth->Solar System->Milky Way Galaxy->Local Cluster->Virgo Cluster->Virgo Supercluster->Laniakea. Thanks to new deep sky surveys, astronomers now think all those places are part of an even bigger cosmic structure in the “neighborhood” called The Shapley Concentration.
Astronomers refer to the Shapley Concentration as a “basin of attraction”. That’s a region loaded with mass that acts as an “attractor”. It’s a region containing many clusters and groups of galaxies and comprises the greatest concentration of matter in the local Universe. All those galaxies, plus dark matter, lend their gravitational influence to the Concentration. There are many of these basins in the Universe, including Laniakea. Astronomers are working to survey them more precisely, which should help provide a more precise map of the largest structures in the Universe.
The Milky Way’s Cosmic Neighborhood
That’s a fascinating possibility! Recent astronomical research suggests that our Milky Way galaxy might be part of an even larger structure than the previously identified Laniakea Supercluster.
Laniakea: Our Galactic Neighborhood
- Laniakea: This massive cosmic structure, spanning hundreds of millions of light-years, was discovered in 2014. It’s a “basin of attraction” where galaxies are drawn together by gravity.
- The Milky Way: Our galaxy is a member of the Local Group, which is itself part of the Virgo Cluster. Both of these are within the Laniakea Supercluster.
A Larger Structure?
New studies have hinted at the possibility that Laniakea might be just one component of an even more colossal structure. One such candidate is the Shapley Supercluster, a massive concentration of galaxies located nearby.
Key points to consider: - Gravitational Influence: If the Milky Way is indeed part of a larger structure, it could significantly alter our understanding of the galaxy’s motion and evolution.
- Cosmic Web: These massive structures are thought to be part of a vast cosmic web, interconnected by filaments of galaxies and dark matter.
- Ongoing Research: Astronomers are continually studying the universe’s large-scale structure to uncover its secrets and understand our place within it.
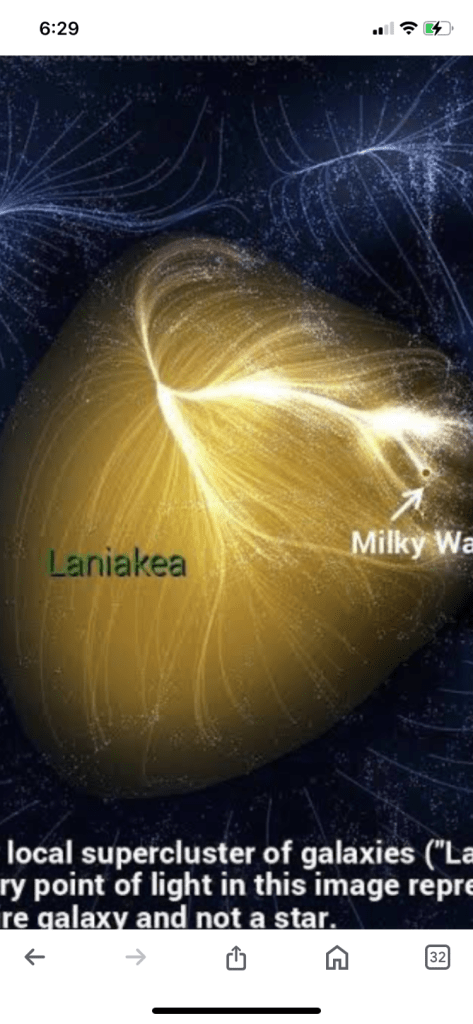
Laniakea is a massive cosmic structure, spanning hundreds of millions of light-years. It’s a “basin of attraction,” meaning that galaxies within it are drawn together by gravity. Think of it as a supercluster of galaxies, a collection of galaxy clusters.
Our Milky Way galaxy is a member of the Local Group, which is itself part of the Virgo Cluster. Both of these are within the Laniakea Supercluster. It’s a vast region of space where galaxies are interconnected by gravity.
The cosmic web is a vast, interconnected network of galaxies, galaxy clusters, and filaments of dark matter that spans the observable universe. It’s often described as a giant cosmic spider web, with galaxies and galaxy clusters clustered at the intersections of filaments.
Think of it as the largest structure in the universe, a cosmic scaffolding that holds everything together. The cosmic web is a result of gravity pulling matter together over billions of years.
The Shapley Supercluster is a massive concentration of galaxies located nearby our own Milky Way galaxy. It’s one of the largest known structures in the universe. The Shapley Supercluster is so massive that its gravitational influence can be felt over hundreds of millions of light-years.
Some astronomers believe that our own Laniakea Supercluster might be a part of the Shapley Supercluster, suggesting that our galaxy is part of an even larger cosmic structure than previously thought.
Is the Laniakea Supercluster the great attractor?
The Great Attractor, in other words, is not so much a THING – like a star, comet or galaxy – but a PLACE, the central gravitational point of the Laniakea supercluster. And that’s where we’re hurtling at a dizzying 600 km/s.
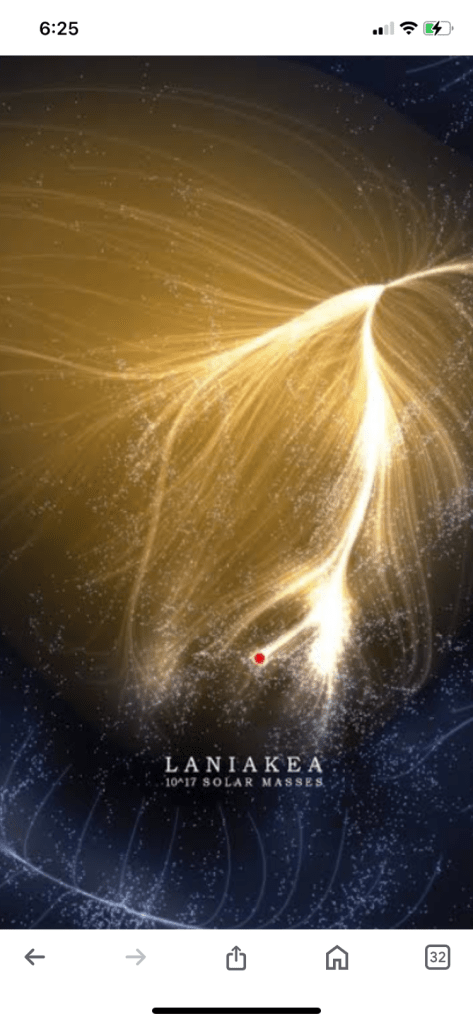
The Cosmicflows team has studied the movements of galaxies and found that the Milky Way is located in a basin of attraction known as Laniakea, which spans 500 million light-years. However, new evidence suggests the possible existence of an even larger structure extending 10 times farther, centered in the Shapley cluster, where the enormous mass is concentrated. These results, published in Nature Astronomy, put into question our current understanding of the structure of the Universe.
According to Oregon State University astronomer Brent Tully, the Universe is like a spider’s web, where galaxies are concentrated in nodes and subject to gravitational forces. By studying cosmic “basins,” scientists can better understand the structure of the Universe, which is thought to be much larger than previously thought
Throughout the last 40 years, there has been a growing appreciation of patterns in the distribution of galaxies in the Universe, reminiscent of geographic features like mountain ranges and island archipelagos. The Milky Way galaxy, with its 100 billion stars, is part of the small Local Group of galaxies, which in turn is a suburb of the Virgo cluster with thousands of galaxies. The Virgo cluster in turn is an outer component of an even larger conglomeration of many rich clusters of galaxies, collectively called the “Great Attractor” because of its immense gravitational pull. In 2014, the team mapped out the Laniakea Supercluster, the bundling of a hundred thousand galaxies over an even larger region, spanning 500 million light years.
The South Pole Wall is as large as the Sloan Great Wall, one of the largest structures known in the Universe, but the new discovery is much closer. University of Paris-Saclay cosmic cartographer Daniel Pomarede, one of the study’s lead authors, explained “One might wonder how such a large and not-so distant structure remained unnoticed. This is due to its location in a region of the sky that has not been completely surveyed, and where direct observations are hindered by foreground patches of galactic dust and clouds. We have found it thanks to its gravitational influence, imprinted in the velocities of a sample of galaxies.”
Please like subscribe comment your precious thoughts on universe discoveries
sk-mania-blogs.in
Full article source google
https://www.buymeacoffee.com/Satyam55
Buy me a coffee!” (your opportunity to say thanks for the free stuff and to encourage me to do even more)
<!– /wp:heading https://www.amazon.in/b?_encoding=UTF8&tag=555101-21&link
“If you like my work or the free stuff on this website and want to say thanks, or encourage me to do more, you can buy me a coffee!
Contribute to my coffee fund with any amount you are comfortable to pay.
The coffee will give me the ‘kick’ to work even harder to empower creative entrepreneurs

Interesting!
LikeLike
🙏🙌🏻
Aum Shanti
LikeLike
Very nformative topic about comet of galaxy ,
LikeLike
Thanks sir 🌺🌺
LikeLike